The formal system of a computer system is called software 1, software or logical medium, which includes all the necessary logical components that allow specific tasks to perform, as opposed to physical members called hardware. The interaction between software and hardware makes a computer (or another device) operational; it sends instructions that the hardware executes, allowing it to function.
Logic components include, among others, computer applications, such as word processing, which allows the user to perform all tasks related to text editing; so-called system software, such as the operating system, which helps the rest of the programs to function correctly, and also facilitating the interaction between the physical components and the rest of the applications and providing an interface with the user.
The vast majority of software writing high-level programming languages. They are more accessible and efficient for programmers to use, as they are closer to natural language than machine language.3 High-level translations are translated into machine language using a compiler or interpreter or a combination of both. It can also be written in assembly language, which is low-level and closely matches machine language instructions; it is translated into machine language using an assembler.
Table of Contents
Definition
Given this definition, the notion of software goes beyond computer programs in their various states: source code, binary or executable; also its documentation, the data to procesing. And even the user’s information is part of the software: that is to say, it encompasses everything intangible, everything that is “non-physical.”
John W. Tukey first used the term software in 1957. In [software] engineering and computer science, it collects information processed by computer systems: programs and data.
So the concept of reading different sequences of instructions (programs) from the memory of a device to control calculations introduce to Charles Babbage as part of his differential motor. The theory which forms the basis of most modern [software] was proposed by Alan Turing in his 1936 essay, “Computable Numbers,” with application to the decision problem.
Software Ranking
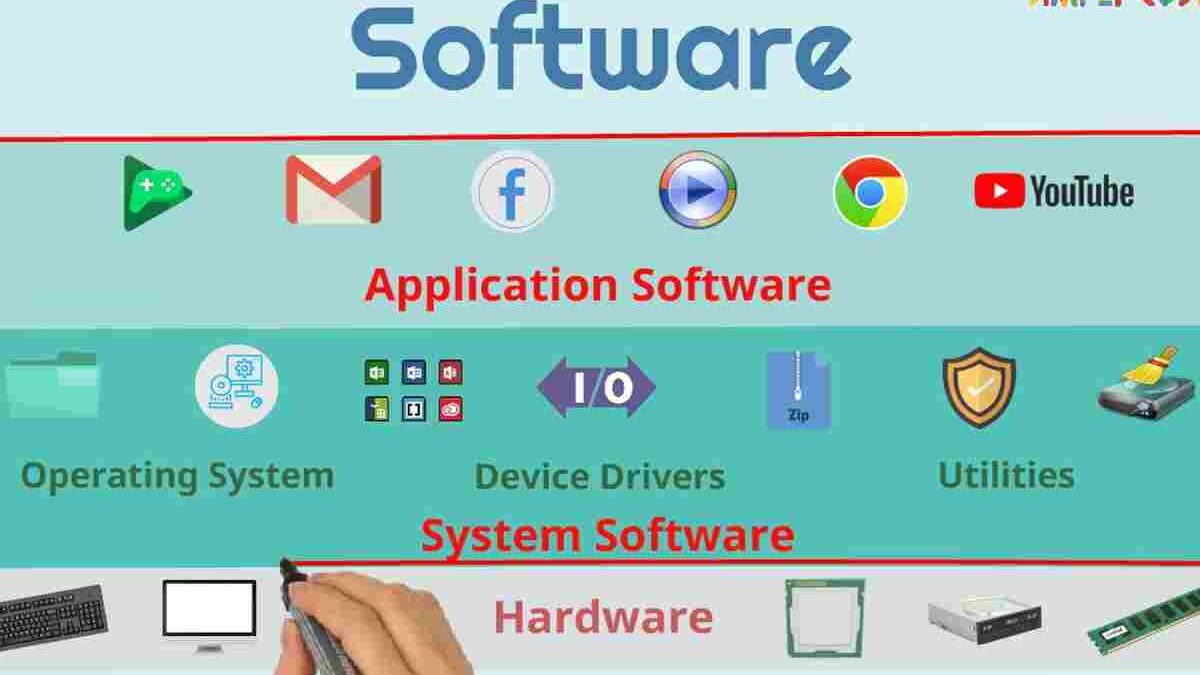
While this distinction is somewhat arbitrary and at times confusing, for practical purposes, it can be classified into three types:
System [software]: Its objective is to properly disconnect the user and the programmer from the details of the particular computer system used by isolating it in particular from the processing related to the internal characteristics of memory, disks, ports and communication devices, printers, screens, keyboards, etc. System [software] provides the user and programmer with appropriate high-level interfaces, drivers, tools, and support utilities that enable maintenance of the entire system. It includes, among others:
- Operating systems
- Device drivers
- Diagnostic tools
- Correction and optimization tools
- Waiters
- Utilities also
Programming Software:
It is the tools that conveniently allow the programmer to develop computer programs using different programming languages and alternatives. They include in basic form:
- Text editors also
- Compilers
- Interpreters
- Connections
- Debuggers
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs): These bundle the previous tools together. Usually, in a visual environment, the programmer does not need to enter multiple commands to compile, interpret, debug, etc. They typically have an advanced graphical user interface (GUI).
Application [software]:
It is the one that allows users to perform one or more specific tasks in any field of activity that can automate or assist. With a particular focus on business. It includes, among others:
- Applications for system control and industrial automation
- Office applications
- Educational software
- Enterprise software11
- Database
- Telecommunications (e.g., Internet and all its logical structure)
- Video game also
- Medical [software]
- Numerical and symbolic calculation [software].
- Assisted design [software] (CAD) and also
- Digital control [software] (CAM)